What are image annotation services?
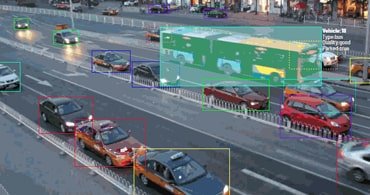
Image annotation services are specialized solutions that involve labeling or tagging various objects, features, or regions within digital images. These services are essential for training artificial intelligence and machine learning models, especially those focused on computer vision tasks such as object detection, facial recognition, and autonomous driving. By meticulously identifying and marking elements like people, vehicles, animals, or specific products within images, annotation services provide the rich data necessary for algorithms to learn and accurately interpret visual information. Imagine a self-driving car needing to differentiate between a pedestrian and a traffic sign; high-quality annotated images make this possible.
Companies often rely on professional image annotation providers who use skilled annotators along with advanced tools to ensure precision and consistency. This process not only accelerates AI development but also boosts the reliability of applications across industries—ranging from healthcare diagnostics to retail analytics. In short, image annotation services form the backbone of many AI-powered innovations by transforming raw visual data into actionable insights that machines can understand and act upon with confidence.

Image Annotation
Why is image annotation important for AI and machine learning?
Image annotation plays a crucial role in the development and success of AI and machine learning systems. By meticulously labeling objects, features, or regions within images, image annotation provides the structured data that algorithms need to recognize patterns and learn from visual information. This process acts as the foundation for computer vision tasks such as object detection, facial recognition, autonomous driving, and medical image analysis.
Without accurately annotated images, AI models would struggle to interpret complex visual data or make reliable predictions. For example, in self-driving cars, annotated images help the system distinguish between pedestrians, traffic signs, and obstacles on the road—ensuring safer navigation. Similarly, in healthcare applications, precise image annotation allows algorithms to identify tumors or anomalies in X-rays with a high degree of accuracy.
Image annotation bridges the gap between raw visual data and meaningful insights by training machine learning models to “see” and understand their environment. Investing time and resources in comprehensive image annotation directly translates into smarter, more reliable AI solutions that can be trusted across a wide range of industries.
What types of image annotation exist?
There are several distinct types of image annotation, each tailored to different needs and applications within fields like computer vision, artificial intelligence, and machine learning. The most common types include bounding box annotation, where objects within an image are marked with rectangular boxes to define their position and size. This method is widely used for object detection tasks, such as identifying cars or pedestrians in autonomous driving systems.
Another prevalent form is semantic segmentation, which involves labeling every pixel in an image according to the category it belongs to—such as road, sky, or building—creating a detailed map for scene understanding. For more precise object boundaries and differentiation between instances of the same class, instance segmentation assigns unique labels to each individual object. Keypoint annotation marks specific points of interest within objects—like facial landmarks on human faces or joint positions on bodies—to facilitate pose estimation and gesture recognition.
Polygonal annotation allows annotators to outline complex shapes by drawing polygons around objects with irregular boundaries for greater accuracy than simple rectangles. line and polyline annotations are used primarily in scenarios such as lane detection on roads or architectural blueprint analysis by tracing straight or curved lines across images. Each type of annotation serves a unique purpose and choosing the right one can dramatically improve the performance of AI systems trained on annotated datasets.